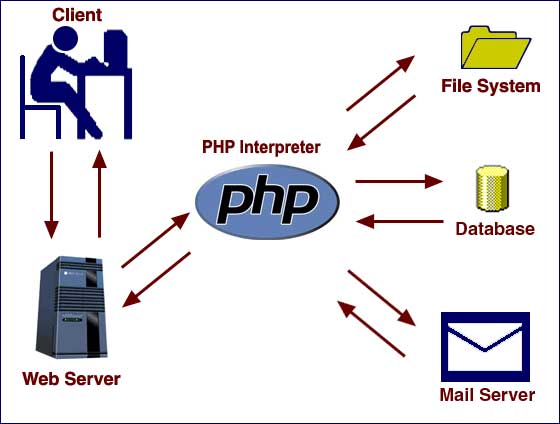
PHP Introduction
PHP started out as a small open source project that evolved as more and more people found out how useful it was. Rasmus Lerdorf unleashed the first version of PHP way back in 1994. PHP is a recursive acronym for "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor". PHP is a server side scripting language that is embedded in HTML. It is used to manage dynamic content, databases, session tracking, even build entire e-commerce sites. It is integrated with a number of popular databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Sybase, Informix, and Microsoft SQL Server.
PHP is pleasingly zippy in its execution, especially when compiled as an Apache module on the Unix side. The MySQL server, once started, executes even very complex queries with huge result sets in record-setting time. PHP supports a large number of major protocols such as POP3, IMAP, and LDAP. PHP4 added support for Java and distributed object architectures (COM and CORBA), making n-tier development a possibility for the first time. PHP is forgiving: PHP language tries to be as forgiving as possible.
PHP Installation
Find a web host with PHP and MySQL support
Install a web server on your own PC, and then install PHP and MySQL
Use a Web Host With PHP Support
If your server has activated support for PHP you do not need to do anything.
Just create some .php files, place them in your web directory, and the server will automatically parse them for you.
You do not need to compile anything or install any extra tools.
Because PHP is free, most web hosts offer PHP support.
Set Up PHP on Your Own PC
However, if your server does not support PHP, you must:
install a web server
install PHP
install a database, such as MySQL
The official PHP website (PHP.net) has installation instructions for PHP: http://php.net/manual/en/install.php
Basic PHP Syntax
A PHP script starts with :
The default file extension for PHP files is ".php".
A PHP file normally contains HTML tags, and some PHP scripting code.
PHP statements end with a semicolon (;).
Debugging
Debugging allows you to step through the execution of your code, monitoring what it does and how it works. It's a bit difficult to explain, unless you've tried it before, and if this is your very first time working with a programming language, you may wish to wait a bit before setting up and using debugging. On the other hand, debugging can be a huge help in finding those pesky bugs, and it will make you a much stronger coder. It's really up to you whether or not you wish to setup debugging now or wait until later on.
In previous chapters, we installed both Apache and PHP on your machine. Thankfully, that's almost everything you need, to make debugging possible for you. In TSW WebCoder, go to the Debug menu and select Setup debugging. You will be presented with a wizard, which will walk you though the entire process of setting up debugging on your machine. It's pretty straight forward, but just in case, I will walk you through the wizard to make sure that everything goes as planned.
1. On the first page, you don't have to do anything. It's simply a welcome screen.
2. On the second page, you should keep the default selection of setting up full debugging.
3. On the third screen, there's a bit of information of Apache and PHP, but since we already installed that, we can just move on.
4. On the fourth screen, you should tell WebCoder where to find your php.ini file. If you followed the directions in this tutorial while installing PHP, and didn't change the path, it should look something like C:\Program Files\PHP\php.ini. Click the browse button to locate it.
5. Now, on the fifth screen, we need a DLL file which will allow PHP and Apache to communicate with the debug client inside of WebCoder. You can get it from http://www.xdebug.org/ by selecting the DLL that fits the version of PHP you installed to the right of the website, under Windows binaries. Download it to the ext directory of your PHP installation, usually C:\Program Files\PHP\ext\. Once it's downloaded, find the path in WebCoder by clicking the browse button to locate it.
6. On the next screen, you should leave the settings as they are, unless you have a specific reason for changing them. The default values should work just fine.
7. Now it's time to modify the php.ini file, to enable the Xdebug module we downloaded. WebCoder will do this for you, if you simply click the Modify button. After the modification, Apache will require a restart to pick up the changes, in case it's already running - this step is rather important, so if it is running, restart it. Otherwise, now would be a fine time to start Apache up.
8. On the next screen, you should locate your document root for Apache in the first textbox, and the localhost path in the second. If you followed this tutorial and didn't change anything, the values entered should look something like this:
Document root: C:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Apache2.2\htdocs\
URL:http://localhost:8080/
9. On the next screen, we can test if everything worked the way it should. Make sure that Apache is started (and restarted, as described after the modification of the php.ini file) and then click the Test button. If everything goes well, you are now ready to debug!
Data types
PHP is a loosely typed language. You don't have to tell the interpreter which type a certain variable is, you just have to assign a value to it, and PHP will know which type to treat it as. In the perfect world, you would never have to care about the type of a variable, but as we all know, the world is far from perfect. There will be many situations where controlling the type of a variable will make sense, and therefore, PHP does expose functions to detect and manipulate the type of a variable. First, a little bit of information about the various types in PHP.
PHP consists of 4 basic data types:
boolean - a boolean is actually much like an integer, but with only two possible values: 0 or 1, which is either false or true.
integer -a number with no decimals, e.g 3 or 42.
float (sometimes referred to as double)-a number that may include decimals, e.g. 42.3 or 10.9.
string A number of characters, which combined makes a text string.
array holds an array of items, e.g. several strings or several integers. An array may contain variables which are arrays which are arrays and so on.
object a reference to an instance of a class. This is related to Object Oriented programming.
resource holds a reference to a special external resource. It may be a file resource, or perhaps an open database connection.
NULL a value of null is nothing. It's not the same as 0 (zero), because that's actually a value. Null is truly nothing. Variables which have not yet been assigned a value, or which you have used the unset() method on, will carry the NULL value. This is useful if you wish to check whether or not a variable contains any value - you may compare it against the NULL constant.